|
This site will post scientific information on glutathione enhancement and supplementation with combination supplements to enhance glutathione such as max gxl, single entity amino acids such as n acetyl cysteine, oral glutathione itself, intravenous glutathione, and bioactive whey protein. According to the MaxGXL patent documents filed in 2001 with the United States Patent office by Dr. Robert Keller, MaxGXL is "N-acetylcysteine, N-acetyl-d-glucosamine, [and] vitamin C whereby the amount of vitamin C is in an amount of at least 1000 mg. or greater to facilitate the absorption of N-acetylcysteine across the cellular membrane; and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier for oral administration". The patent documents on Max GXL further state that MaxGXL will contain: "one or more of the following substances from the group consisting of alpha-lipoic acid, sylmarin, quercitin, l-glutamine, a probiotic, and dietary protein...to stimulate the natural production of glutathione".
The MaxGXL patent document mentions a number of disease states associated with reduced glutathione levels, but Max GXL has not been studied in the treatment of these diseases, and no disease treatment claims can scientifically or legally be made based on the Max GXL patent document. The Patent states:
Per packet of 3 capsules:L-glutamine (750 mg); N Acetyl Cysteine (375 mg); Cordyceps (300 mg); Vitamin C (250 mg); N Acetyl D-glucosamine (125 mg); Conjugated Linoleic Acid (100 mg); Quercetin (37.5 mg); Alpha Lipoic Acid (75 mg); Milk Thistle Extract (Silymarin), (25 mg); gelatin (capsules).  The Recommended dose of Max GXL is 6 capsules per day (3 in the morning and a packet of 3 in the evening). If you are considering taking a larger dose, consult your physician or health care practitioner. Max GXL is supplied bottles of 180 capsules. The recommended dose is 6 capsules per day in divided doses of 3 capsules in the AM and 3 capsules in the PM. At the recommended dose of 6 capsules per day, a bottle of 180 capsules of Max GXL will last for 30 days  Max GXL was previously supplied in packets of 3 capsules each. There are 56 of these packets in each box of MaxGXL, and at the recommended dose of 2 packets per day, a box of Max GXL will last for 28 days. Max GXL is a nutritional supplement and not a drug. The FDA does not approve nutritional supplements. Max GXL (like all nutritional supplements) cannot make a claim to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent disease. The manufacturer makes these statements regarding MaxGXL: Max GXL Product Statement and Benefits We were not able to find any clinical or scientific studies or medical reviews of Max GXL published in the National Library of Medicine (MEDLINE) using a PubMed search. Additionally, we were not able to find any ongoing or future planned clinical trials or medical trials of MaxGXL. The manufacturer does list an unpublished study of Max GXL of an unknown number of patients (n=?), divided into 4 test groups who were studied from 3 to 6 months. The manufacturer states: "The graph below shows the increase in glutathione levels experienced by 4 groups of patients. Group 1 (normal health patients) were tested after 6 months of use, while Groups 2, 3 and 4 (HIV, Hepatitis C, and Chronic Viral Illness respectively) were tested after only 3 months of the MaxGXL regimen". Because the study period was significantly longer for study participants with normal health (twice as long), it is difficult to compare this group to the other 3 groups who were studied for a much briefer period of time. All four groups did have a substantial increase in their blood lymphocyte glutathione levels (416%, 347%, 270% and 262% after 3 months, 6 months, 6 months, and 6 months respectively in normal volunteers, HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) patients, HCV (Hepatitis C virus) patients, and CFIDS/chronic viral illness patients), but p values (statistical significance) of these results were not provided. Because this product is a nutritional supplement, no medical claims were made by the manufacturer for these results. 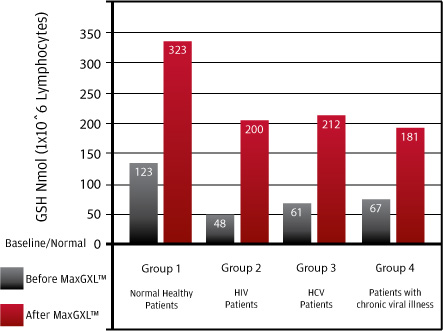 Although there are no published studies on Max GXL itself, there are numerous published studies on its components, which are listed here in descending order of their concentration in Max GXL: L-glutamine; N Acetyl Cysteine; Cordyceps; Vitamin C; N Acetyl D-glucosamine; Conjugated Linoleic Acid; Quercetin; Alpha Lipoic Acid; Milk Thistle Extract (Silymarin). Max GXL is distributed through network marketing. It is not available in stores. The manufacturer does not require that customers sign up as a MaxGxl distributor to get discounts on this product, but the best discounts are available through a monthly automatic shipment, or the "Loyalty" program, ("preferred customer") program. The manufacturer will allow customers to cancel their automatic shipment at any time, without penalty or obligation.  It is difficult to make a scientifically accurate "blanket statement" on the safety of a supplement that contains multiple ingredients without doing significant research on each individual ingredient, and then researching safety on the combination of those ingredients within a single supplement. That being said, there does not appear to be any single ingredient within Max GXL that would suggest that the supplement is unsafe. There are cautions on supplementing with some of the individual ingredients contained in Max GXL, however. The Physician's desk Reference (PDR), states that alpha lipoic acid (an ingredient in Max GXL) should be avoided in pregnancy, and used with caution in diabetics, and in patients with glucose intolerance: "Because of lack of long-term safety data, alpha-lipoic acid should be avoided by pregnant women and nursing mothers. Those with diabetes and problems with glucose intolerance are cautioned that supplemental alpha-lipoic acid may lower blood glucose levels. Blood glucose should be monitored and antidiabetic drug dose adjusted, if necessary, to avoide possible hypoglycemia." Physicians Desk Reference safety statement on alpha lipoic acid PRECAUTIONS for NAC:The Physician's desk Reference (PDR), states that acteylcysteine (NAC, an ingredient in Max GXL) should be avoided in nursing mothers and should only be used in pregnancy on the advice of a physician. It should be used with caution in patients with chronic liver disease, as well as in pre-term newborns, and may be harmful if administered early in the treatment of critically ill patients. The supplement may cause headaches and (rarely) kidney stones. NAC should be used with caution in those with a history ulcers. Additionally, NAC may interact with some medications including nitrates, and carbamazepine. No interactions with nutritional supplements, food or herbs have been reported. "Supplemental NAC should be avoided by nursing mothers and should only be used by pregnant women if prescribed by a physician. N-acetylcysteine clearance is reduced in those with chronic liver disease as well as in pre-term newborns. NAC may be harmful if administered early in the treatment of critically ill patients. NAC may intensify headaches in those taking nitrates for the treatment of angina. Although the incidence of cystine renal stones is low, they do occur. Those who do form renal stones, particularly cystine stones, should avoid NAC supplements. NAC and its sulfhydryl metabolites, like other sulfhydryl-containing substances, could produce a false-positive result in the nitroprusside test for ketone bodies used in diabetes. NAC should be used with caution in those with a history of peptic ulcer disease, since mucolytic agents may disrupt the gastric mucosal barrier." "Adverse reactions reported with oral NAC include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headache (especially when used along with nitrates) and rashes. There are rare reports of renal stone formation. Adverse reactions reported with intravenous NAC include bronchospasm, nausea, vomiting, stomatitis, rhinorrhea, headache, tinnitus, urticaria, rashes, chills and fever. There are rare reports of anaphylactic reactions. The most common symptoms of those experiencing anaphylactoid reactions are rash, pruritis, flushing, nausea, vomiting, angioedema, tachycardia, bronchospasm, hypotension, hypertension and ECG change. The anaphylactoid reactions are pseudo-allergic rather than immunologic." Interactions for NAC: "Nitrates: Use of supplemental NAC along with nitrates may cause headaches. Carbamazepine: Use of supplemental NAC along with carbamazepine may cause reduced serum levels of carbamazepine. No interactions with nutritional supplements, food or herbs are known." Animal studies showing adverse effects of NAC: According to research conducted at the University of Virginia Health System, N-acetylcysteine (NAC) can form a red blood cell-derived molecule that makes blood vessels think they are not getting sufficient oxygen. This leads to the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a serious condition characterized by high blood pressure in the arteries that carry blood to the lungs. Adverse effects seen in animal studies may not necesarily apply to humans, however it might be more prudent for patients with this type of hypertension to take a bioactive whey protein to increase glutathione rather than to use Max Gxl or other supplements containing NAC. Source: Journal of Clinical Investigation September, 2007; 117(9):2592-601 PDR Safety Statements on individual ingredients in Max GXL: Physicians Desk Reference safety statement on acetylcysteine (NAC) Physicians Desk Reference safety statement on Cordyceps Physicians Desk Reference safety statement on L Glutamine Physicians Desk Reference safety statement on N Acetyl Glucosamine Physicians Desk Reference safety statement on Conjugated Linoleic Acid Physicians Desk Reference safety statement on Quercetin Physicians Desk Reference safety statement on Silymarin (Milk Thistle) If the buyer purchases Max GXL through the automatic shipment ("Loyalty") program (the most economical means), a bottle of 180 capsules of Max GXL costs $50 and the daily cost is $1.67. Shipping is a flat rate of $9.95 per order (FEDEX ground), but this shipping cost does not increase, regardless of how many boxes are purchased, so save money by ordering for each member of your family. You will need a sponsor username to order the product. Our sponsor username for the current month is: 114882 You can order online here: Order Max GXL online here  Ordering Max GXL by Phone To order by phone 8 AM-10 PM PST: 800-833-3220 801-316-6380 (customer care) Max GXL Bonnie Overson The Villages, Florida Distributor #114882 Special Promotion: Ask for a FREE CD or DVD about the benefits of glutathione enhancement! Sign up as a Max GXL Distributor or select Max Loyalty customer program and buy for as low as $50 Sign up as a Max GXL Preferred customer and buy for $50 Purchase Max GXL at retail price (no automatic shipment) for $69 Download FREE information on glutathione enhancement |